Answers: no and let us see the jump effect.
This is the most popular stochastic process, underlying the famous Black-Scholes-Merton options equation.

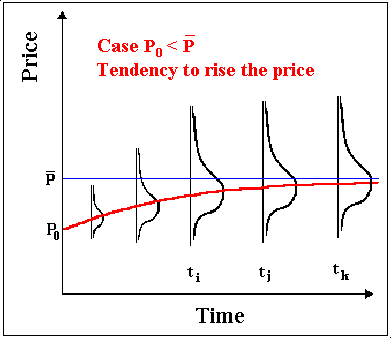
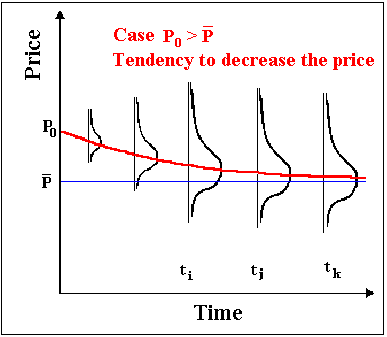
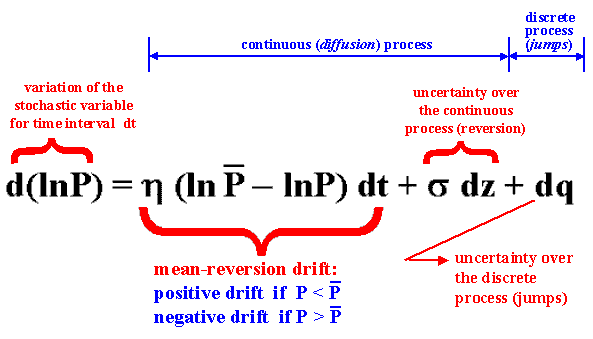
In this process, the price tends to revert toward a long-run average price (or an equilibrium level) P.
The picture below shows jumps (up and down) in the oil prices history (Brent and Similar Oils, 1970-1999).
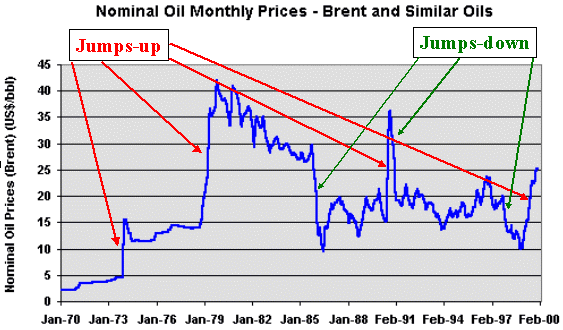
We see oil prices jumps in both directions, depending of the kind of abnormal news: jumps-up in 1973/4, 1978/9, 1990, 1999; and jumps-down in 1986, 1991, 1997.
Mean-Reversion + Jumps for Oil Prices
Was adopted in the Marlim Project Finance (equity modeling) offshore Brazil a mean-reverting process with jumps:
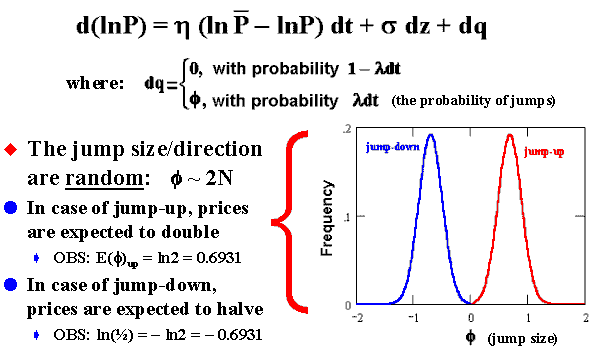
The interpretation of the jump-reversion equation is:
See more in the webpage on stochastic processes.
Now the risk premium comparison between these stochastic processes
(for the definition of risk premium, see FAQ 1).
The chart below compares mean-reversion (red line) with GBM (blue line)
for an at-the-money project at current 25 $/bbl. The option (F) expires in
three years (black line is the max. (NPV, 0) at expiration).
NPV is expected to revert from zero to a negative value (because the long
run mean is assumed 20 $/bbl, and in this case the project has a negative
NPV):
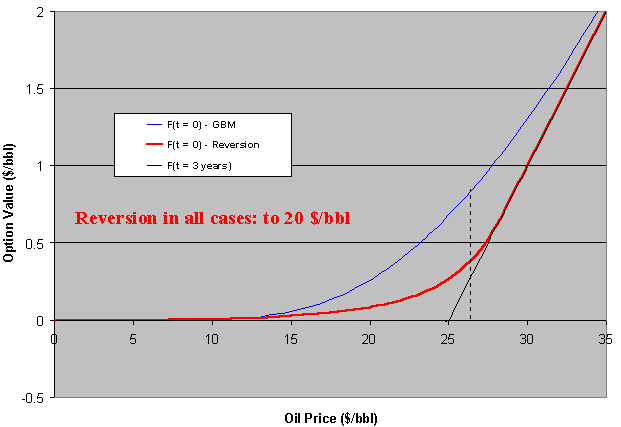
The option value (F) here is normalized by the number of barrels of the undeveloped oil reserve (so is per barrel). In order to get the undeveloped field option value, just multiply F by the reserve size.
In the case above the GBM premium is always above the mean-reverting one. But this is not general. We'll see that if the reversion is toward a positive NPV, the option premium can be higher than GBM one. But first let us see the same case above with jumps.
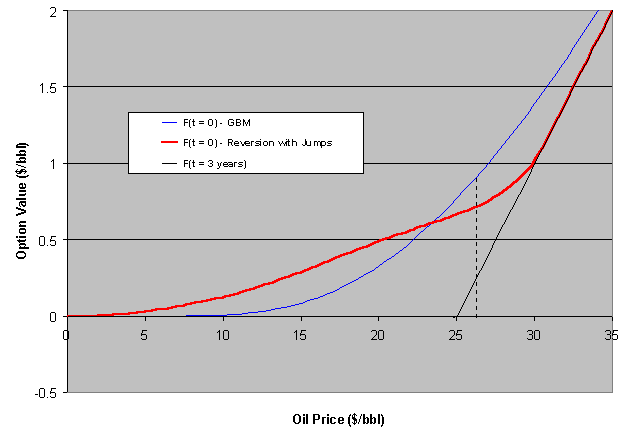
The jumps added to the reversion process increase the option premium even being neutral jumps (jumps up and down so that the mean jump is zero). Now there is a region that the reversion + jump premium is higher than GBM one.
The chart below compares the mean-reversion (without jumps) with GBM for
an at-the-money project at current 15 $/bbl (suppose).
In this case the project NPV is expected to revert from zero to a
positive value.
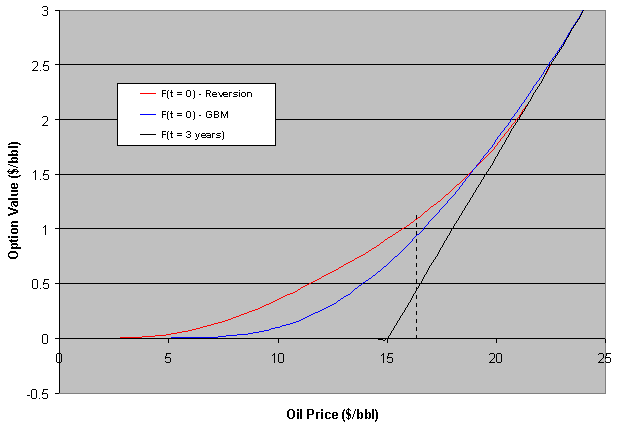
In this case the mean-reversion premium is higher than GBM one for an important region in the chart. For high oil prices, there is an inversion because the reverting drift is weak or even negative (the reversion is toward 20$/bbl in all these examples).
In this case, what happen if is added jumps into the mean-reversion process? Again, even for neutral jumps (jumps with zero mean) the risk-premium rises:
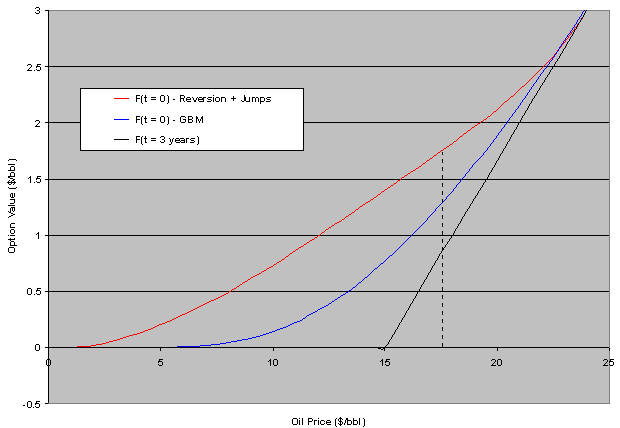
In these examples, when adding jumps, the volatility of the GBM was increased in order to compare GBM x reversion+jumps with rough equivalent volatilities.
![]()